Propionic Acid: Properties, Reactions, Production and Uses
Propionic acid is a naturally occurring short-chain carboxylic acid with the formula CH3CH2COOH. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor, often described as resembling sweat or cheese.
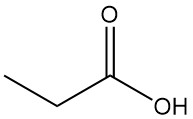
Propionic acid is a naturally occurring short-chain carboxylic acid with the formula CH3CH2COOH. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor, often described as resembling sweat or cheese.
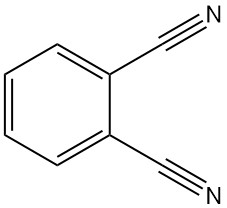
Phthalonitrile, also known as 1,2-dicyanobenzene or 1,2-benzenedicarbonitrile, is an organic compound with the formula C8H4N2. It is a crystalline powder with a faint grayish yellow color and a slight aromatic odor, similar to benzonitrile.
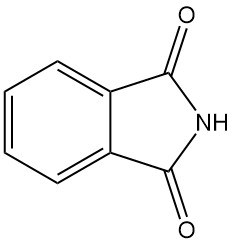
Phthalimide, also known as 1,3-dioxoisoindoline, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H5O2N. It is a white solid that is slightly soluble in water and soluble in basic solutions.
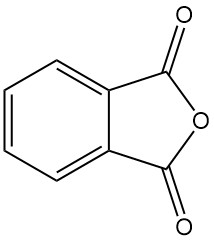
Phthalic anhydride [85-44-9], also known as isobenzofuran-1,3-dione, is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2O. It is a colorless to white, solid in the form of needles with a mild, distinctive odor that is formed by the dehydration of phthalic acid.
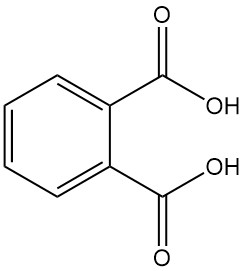
Phthalic acid, also known as o-phthalic acid or 1,2-benzenedicarboxylic acid, is an aromatic dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C8H6O4. It is a white, crystalline solid that is not important industrially. It is formed as a byproduct in the manufacture of phthalic anhydride.
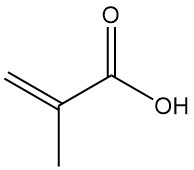
Methacrylic acid, also known as α-methylacrylic acid or 2-methylpropenoic acid, is an organic acid with the formula CH2=C(CH3)COOH. It is a colorless, moderately volatile, corrosive liquid with a strongly acrid odor.
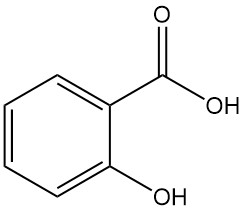
Salicylic acid, also known as 2-hydroxybenzoic acid or o-hydroxybenzoic acid, is an aromatic compound with the formula C7H6O3. It is a colorless, odorless, crystalline solid that is found naturally in many plants, primarily as esters.
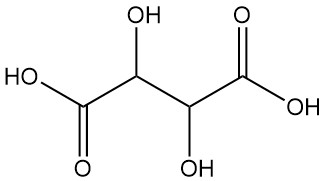
Tartaric acid, also known as acidum tartaricum, 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioic acid (IUPAC nomenclature), is a white crystalline organic acid found naturally in many fruits with the formula C4H6O6. The molecule possesses two asymmetric carbon centers with two carboxylic acid groups and a dialcohol in the same molecule, resulting in four stereoisomers.
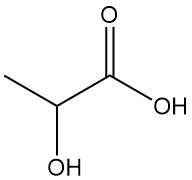
Lactic acid, also known as 2-hydroxypropionic acid, is a natural organic acid with the molecular formula CH3CH(OH)COOH. Pure lactic acid is a white, crystalline solid with a low melting point that is found in many biological systems, including the human body.
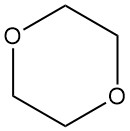
Dioxane, or 1,4-dioxane, is a heterocyclic diether with the formula C4H8O2. It is a flammable, colorless liquid with a faint, sweet odor similar to diethyl ether. It is known by other names such as p-dioxane, diethylene oxide, diethylene dioxide, diethylene ether, 1,4-dioxacyclohexane, dioxyethylene ether, and dioxan.
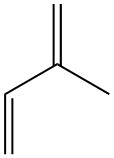
Isoprene, also known as 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a five-carbon hydrocarbon that exists in nature at trace levels. It is a colorless, volatile liquid with the chemical formula C5H8.
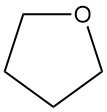
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), also known as oxolane, is a cyclic ether with the chemical formula C4H8O. It has a wide application in the chemical industry.