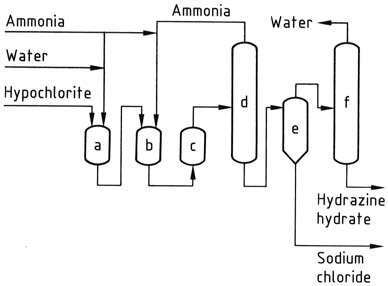
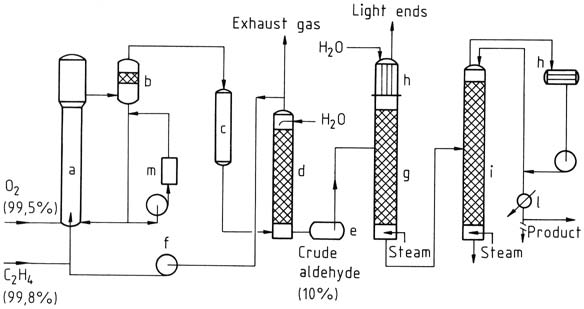
Acetic anhydride: Properties, Reactions, Production and Uses
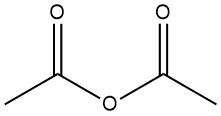
Acetic anhydride is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3CO)2O. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor and is commonly used as an acetylating agent and a dehydrating agent.