Uses of Methanol
Methanol is a highly versatile chemical with many uses. It is used as a fuel, a solvent, and a building block for many other chemicals and is also a renewable energy source.

Methanol is a highly versatile chemical with many uses. It is used as a fuel, a solvent, and a building block for many other chemicals and is also a renewable energy source.
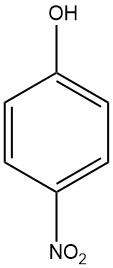
4-Nitrophenol, also known as p-nitrophenol or 4-hydroxynitrobenzene, is an aromatic compound with the chemical formula C6H5NO3. It is a yellow to colorless crystalline solid with a sweet, phenolic odor. It is soluble in water, ethanol, and other organic solvents.

3-hydroxybezoic acid is one of three isomers of hydroxybenzoic acid, the other two being 2-hydroxybenzoic acid and 4-hydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C7H6O3. It is also known as m-hydroxybenzoic acid or m-salicylic acid. It is a white, odorless solid that is soluble in water and ethanol.

4-hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as para-hydroxybenzoic acid, is an aromatic organic acid with the chemical formula C7H6O3. It is a white or colorless solid that is soluble in water, ethanol, and other polar solvents.

3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid, also known as protocatechuic acid, is a naturally occurring organic acid with the formula C7H6O4. It is a white or slightly off-white crystalline solid that is soluble in some organic solvents like ethanol and ether, but insoluble in water.

Antioxidants are used in four primary categories of substrates: foods, fuels, lubricants, and polymers. Each category has its own specific antioxidant products, but some antioxidants can be used in multiple categories.

Neutral dyes are those that do not change the pH of the solution in which they are dissolved. They are often used to dye synthetic fibers, such as polyester and nylon, which are not affected by acidic or alkaline dyes.

Antimony trioxide (Sb2O3) is a white crystalline powder with a molar mass of 291.52 g/mol and a melting point of 656°C. It has two forms: senarmontite (below 570°C) and valentinite (above 570°C).

Antifreeze is a substance used to lower the freezing point of water or water-based liquids. It is most commonly used to protect internal combustion engines from freezing, but it also has other applications in refrigeration, heat transfer systems, water heaters, and more.

Arsenic compounds are generally toxic, especially inorganic ones. Some organic arsenic compounds used as chemical weapons are also highly toxic, but naturally occurring organic arsenic compounds in seafood are less so.

Arsenic trioxide, also known as white arsenic, is a highly toxic substance with a chemical formula of As2O3 and a molecular weight of 197.8 g/mol. It exists in three forms: two crystalline and one amorphous.
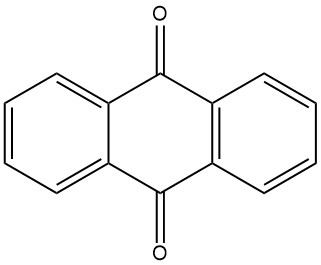
Anthraquinone is an organic compound with the formula C14H8O2. It is a yellow, crystalline solid that is nearly insoluble in water and organic solvents at room temperature. Its solubility increases with temperature.