Tetrahydrofuran (THF): Properties, Reactions, Production and Uses
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), also known as oxolane, is a cyclic ether with the chemical formula C4H8O. It has a wide application in the chemical industry.
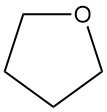
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), also known as oxolane, is a cyclic ether with the chemical formula C4H8O. It has a wide application in the chemical industry.
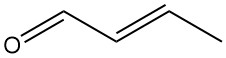
Crotonaldehyde [4170-30-3], also known as 2-butenal, is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor and strong lacrimatory properties. It has a chemical formula of CH3CH=CHCHO, and it exists as two stereoisomers: cis-crotonaldehyde [15798-64-8] and trans-crotonaldehyde [123-73-9].
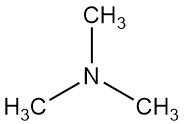
Trimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula N(CH3)3. It is a colorless gas or compressed liquid with a strong fishy odor, at low concentrations. At higher concentrations, the odor becomes more ammonia-like.
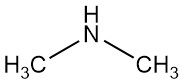
Dimethylamine is an organic compound with the formula (CH₃)₂NH. It is a colorless, flammable gas with an ammonia-like odor, although at low concentrations it can smell like fish, and its odor is more potent than methylamine and less than trimethylamine. Dimethylamine is commonly encountered commercially as a solution in water at concentrations up to around 40%.
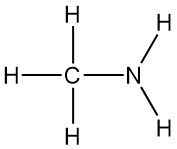
Methylamine is the simplest primary amine, with the formula CH3NH2. It’s a colorless gas that’s derived from ammonia, with one hydrogen atom replaced by a methyl group. It was first synthesized in 1849 by Wurtz alongside dimethylamine and trimethylamine.
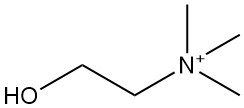
Choline [62-49-7], also known as trimethyl(2-hydroxyethyl)ammonium hydroxide, is a quaternary ammonium compound with the molecular formula C₅H₁₅O₂N. It was first isolated from pig bile in 1849 by Stecker and is subsequently found in brain tissue.
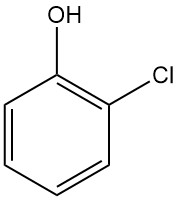
2-Chlorophenol, also known as ortho-chlorophenol, is an aromatic compound with the chemical formula C6H4ClOH. It is a liquid with a strong, unpleasant odor.

Propylene chlorohydrin is a general term that refers to the two isomers of chloropropanol (1-chloro-2-propanol and 2-chloro-l-propanol) with the chemical formula C3H7ClO. It is a colorless liquid with a pleasant odor, and it is soluble in water and organic solvents.

2-Chloroethanol, also known as ethylene chlorohydrin, is an organic chemical compound with the formula HOCH2CH2Cl. It is a colorless liquid with a pleasant odor that was an important intermediate used in the past to produce ethylene oxide, but that is no longer the case.
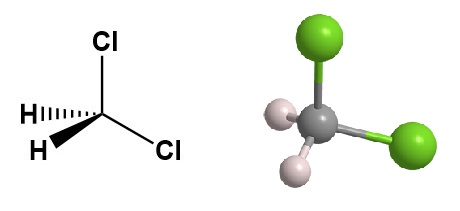
Dichloromethane, also known as methylene chloride, or DCM, is a colorless, highly volatile liquid with a sweet, chloroform-like odor. Its chemical formula is CH2Cl2, and it is a widely used industrial solvent with a variety of applications. It represents 25% of the total production of chloromethanes (CH3Cl, CH2Cl2, CHCl3, and CCl4).
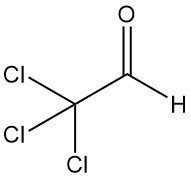
Trichloroacetaldehyde [75-87-6], also known as chloral or 2,2,2-trichloroethanal, is an organic compound with the formula CCl3CHO. It is a colorless liquid that was first produced in 1832 by Justus von Liebig through the chlorination of ethanol.

Dichloroacetaldehyde [79-02-7], or 2,2-dichloroethanal, is a chlorinated acetaldehyde with the chemical formula Cl2CHCHO. It is a colorless liquid with a pungent, irritating odor that was produced for the first time in 1868 by F. Paterno by distillation of dichlorodiethyl acetal, CHCl2CH(OC2H5)2, with sulfuric acid.