Bleaching Powder: Production and Uses
Solid hypochlorite is a soft, white, dry powder. It is almost odorless or smell more or less strongly of chlorine or hydrochloric acid because of decomposition during storage.
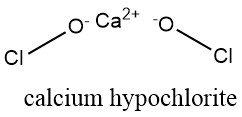
Solid hypochlorite is a soft, white, dry powder. It is almost odorless or smell more or less strongly of chlorine or hydrochloric acid because of decomposition during storage.
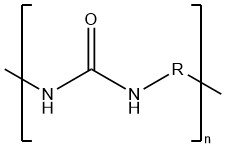
Polyureas refer to polymers with ureylene groups–NHCONH–in their polymer chain. Linear polyureas are thermoplastic polycondensation products, featuring either aromatic (R = arylene) or aliphatic (R = alkylene) structures.

Thiamin chloride hydrochloride (Vitamin B1) is a white crystalline material. It crystallizes as colorless monoclinic needles. It has a characteristic odor and a slightly bitter taste.
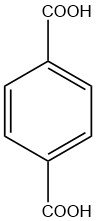
Terephthalic acid is an organic diacid with the chemical formula C6H4(CO2H)2. It is a white crystalline solid classified as commodity chemical, Terephthalic acid exists commercially in a free-flowing powder form that comprises rounded crystals. When recrystallized slowly, it forms needles.

Glyoxylic acid, also known as oxoacetic acid, is the simplest α-oxocarboxylic acid with the formula C2H2O3. It is a colorless solid that is present in plants and plays an important role in animal metabolic cycles.
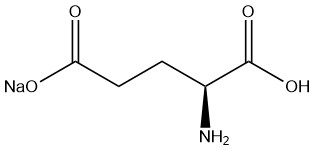
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is the sodium salt of L-glutamic acid; it is used as a flavor enhancer with a global production of 3 million tonnes.

Originally the term metallic soaps was only used for metal salts of fatty acids of naturally occurring animal fats (mainly tallow and lard) and vegetable fats.

Gelatin is a translucent, colorless, brittle (when dry), flavorless, edible, multifunctional protein polymer, hot-water extracted from “collagens” obtained from various animal and fish byproducts.
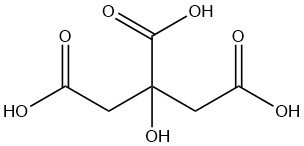
Citric acid is a weak organic acid found naturally in citrus fruits, especially lemons and limes. It is a colorless, crystalline solid at room temperature with the formula C6H8O7.
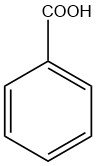
Benzoic acid is a white crystalline solid organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5COOH. The name “benzoic acid” is derived from gum benzoin, a resinous substance obtained from the styrax plant indigenous to South Asia.

Acetone, also known as 2-propanone, is a colorless, flammable liquid with a pungent odor and low viscosity. It is the simplest ketone, with the formula C3H6O. Acetone is miscible with water, meaning it mixes readily with water in any proportion.
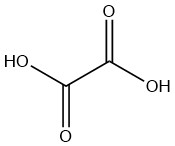
Oxalic acid is the simplest saturated dicarboxylic acid with the formula C2H2O4. It is a white solid that occurs naturally in the form of a dihydrate. Anhydrous compound must be produced from the dihydrate even when manufactured industrially.