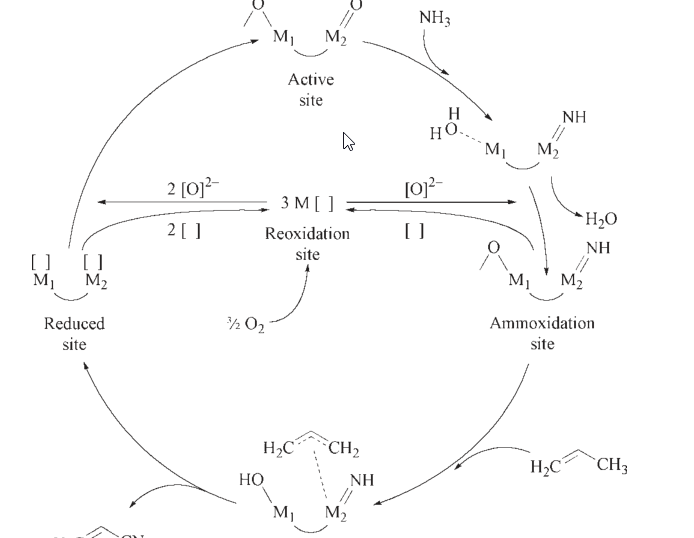
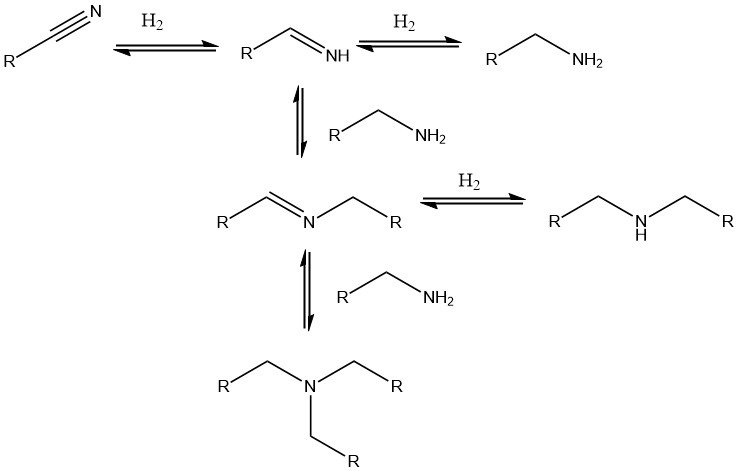
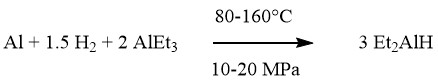Nitration of Aromatic Compounds
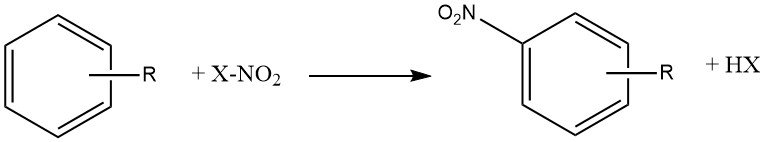
The nitration reaction is a chemical process in which one or more nitro (NO2) groups are introduced into an aromatic nucleus by replacing a hydrogen atom. It is an electrophilic substitution reaction commonly used to modify aromatic compounds by attaching nitro groups, which can significantly alter their properties and reactivity.