Acetaldehyde: Properties, Reactions and Uses
Acetaldehyde, also known as ethanal, is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO. It is a volatile, low-boiling, and highly flammable liquid characterized by its strong odor.
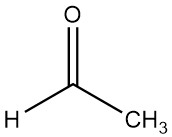
Acetaldehyde, also known as ethanal, is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO. It is a volatile, low-boiling, and highly flammable liquid characterized by its strong odor.
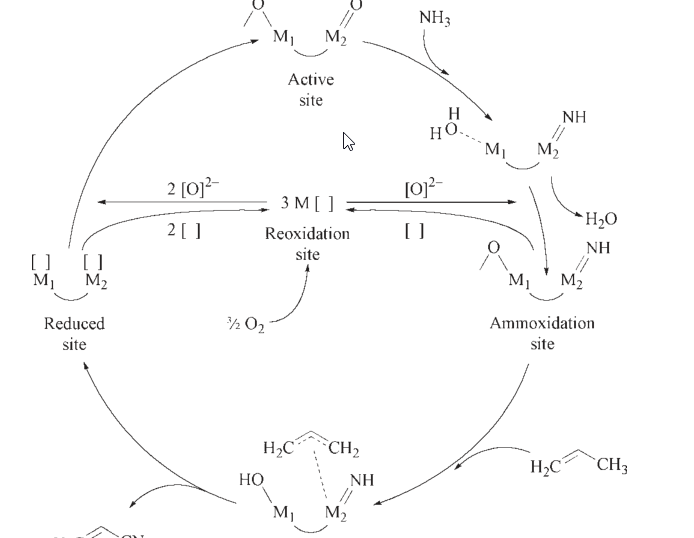
They are employed in the production of synthesis gas and hydrogen, ammonia, methanol, and Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, in the transformation of hydrocarbons (epoxidation of ethylene and propene, ammoxidation of hydrocarbons, and hydroprocessing reactions), as environmental catalysts for catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides from stationary sources, and in automotive exhaust catalysis.

Green ammonia is described as ammonia synthesized with essentially zero carbon ootprint. Green ammonia can be produced using conventional technology for the ammonia synthesis loop in combination with electrolysis-based hydrogen or using nonconventional technologies for ammonia synthesis.
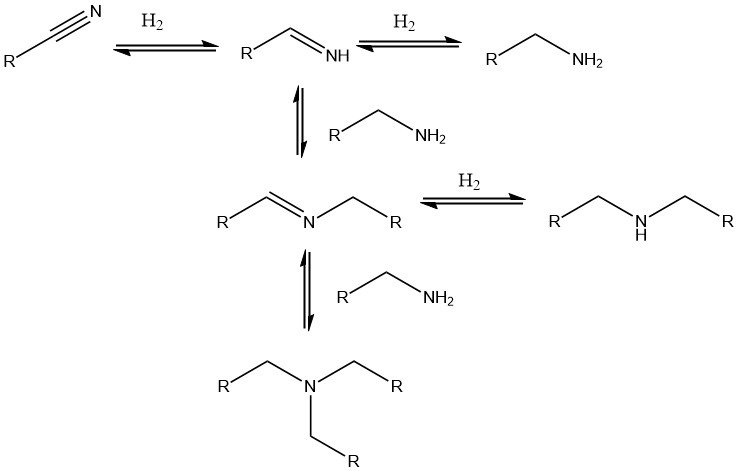
Aliphatic amines are produced from alcohols, carbonyl compounds, nitriles, alkyl halides, nitro compounds and olefins. The production of amines involves different methods, each suited to specific raw materials and desired products.

1. amines Salts Formation, 2. Conversion to Carboxamides, 3. Conversion to Sulfonamides, 4. Reaction with Carbonyl Compounds, 5. Reaction with Carbon Dioxide and Carbon Disulfide
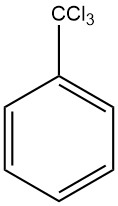
Benzotrichloride is the product resulting from exhaustive chlorination of the side chain of toluene also known as trichloromethylbenzene, α,α,α-trichlorotoluene and phenyl chloroform. It is a chemical compound with the formula C7H5Cl3.

Solid glycolic acid is the simplest α-hydroxycarboxylic acid with the formula C2H4O3. It forms colorless, monoclinic, prismatic crystals. This acid exhibits high solubility in various solvents, including water, methanol, ethanol, acetone, and ethyl acetate.

Nitrobenzoic acids are derivatives of benzoic acid with the general formula C7H5NO4. Two isomers (meta and para) are commercially important. Nitrobenzoic acids are about ten times more acidic than benzoic acid because of the presence of the nitro groupe.
Methanol, also known as wood alcohol, is a chemical compound with the formula CH3OH. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive alcoholic odor. Methanol is the simplest alcohol, and it is the most important alcohol industrially.
Ethanol, also known as ethyl alcohol, is one of the most important alcohols, with the chemical formula CH3CH2OH. It is a colorless, volatile liquid with a characteristic odor and is widely used in a diverse range of applications. Other names of ethanol include alcohol spirit, spirit of wine, grain alcohol, absolute alcohol, and ethyl hydrate.

Butanal, also known as butyraldehyde, is an organic compound with the formula CH3(CH2)2CHO. It is a colorless flammable liquid with a strong, unpleasant odor, often described as bready, cheesy, or buttery.

Acetic acid is a clear, colorless, corrosive liquid that has a pungent odor and is a dangerous vesicant. It is found in dilute solutions in many plant and animal systems.