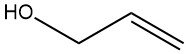
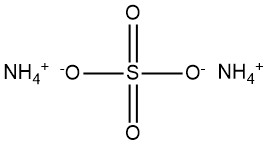
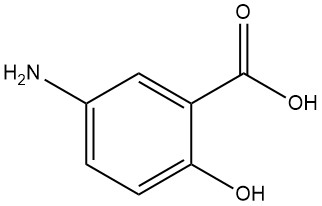
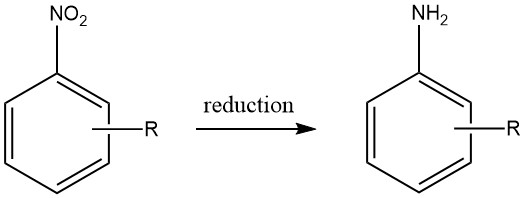
Aluminum Chloride: Properties, Production and Uses
Hans Christian Oersted first prepared anhydrous aluminum chloride in 1825 by passing chlorine gas through a heated mixture of alumina and carbon. This compound is a significant catalyst in organic chemistry, particularly for Friedel-Crafts alkylation and acylation, which are used to produce alkylated aromatics, dyestuffs, pharmaceuticals, and perfumery chemicals.