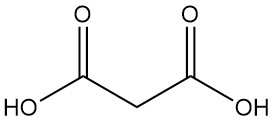
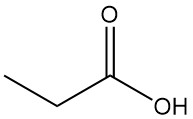
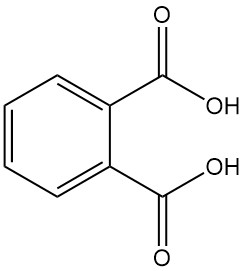
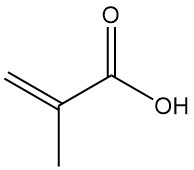
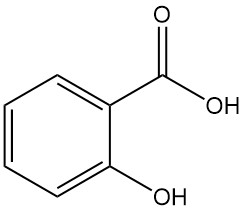
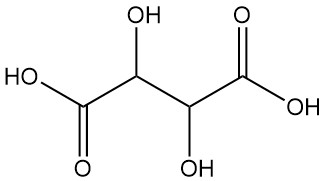
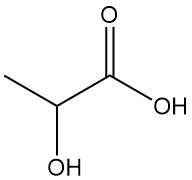
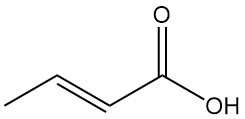
Gluconic Acid: Properties, Reaction, Production and Uses
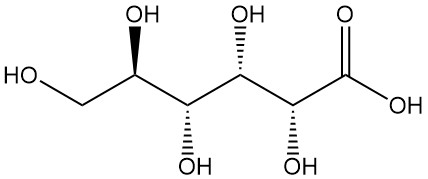
Gluconic acid, also known as 1,2,3,4,5-pentahydroxy pentane-1-carboxylic acid, is an organic acid with the formula C6H12O7. It is a white, odorless, crystalline powder that is naturally found in humans and other organisms and also in food products such as wine and honey.