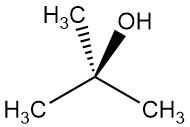
2-Methyl-2-propanol: Properties, Production and Uses
2-Methyl-2-propanol, also known as tert-butanol, is the simplest tertiary alcohol with the chemical formulat (CH3)3COH. It is a colorless, solid crystal at room temperature. However, it melts near room temperature (26 °C) to become a viscous liquid with a camphor-like odor.