Phenol: Production, Reactions and Uses
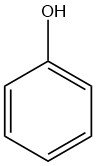
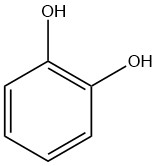
Phenol, also known as hydroxybenzene, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid at room temperature, but technical grade phenol can be a liquid due to impurities. It has a distinct odor, often described as sickeningly sweet and tarry.