Citric acid: production, reactions and uses
Citric acid is a weak organic acid found naturally in citrus fruits, especially lemons and limes. It is a colorless, crystalline solid at room temperature with the formula C6H8O7.
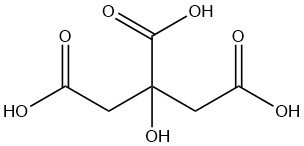
Citric acid is a weak organic acid found naturally in citrus fruits, especially lemons and limes. It is a colorless, crystalline solid at room temperature with the formula C6H8O7.
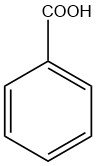
Benzoic acid is a white crystalline solid organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5COOH. The name “benzoic acid” is derived from gum benzoin, a resinous substance obtained from the styrax plant indigenous to South Asia.
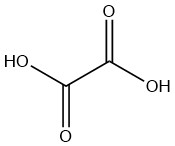
Oxalic acid is the simplest saturated dicarboxylic acid with the formula C2H2O4. It is a white solid that occurs naturally in the form of a dihydrate. Anhydrous compound must be produced from the dihydrate even when manufactured industrially.

Dichloroacetic acid is a colorless and highly corrosive liquid it emits acidic vapors that can cause irritation to the mucous membranes. It exhibits complete miscibility with water and can dissolve readily in various organic solvents such as alcohols, ketones, hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
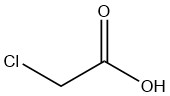
Chloroacetic Acid is an organic compound with the formula CH2ClCOOH. It is a colorless, hygroscopic crystalline solid that exists in various crystalline forms.