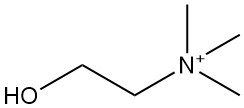
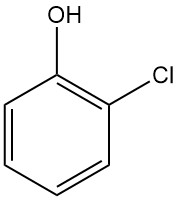
Crotonic Acid: Properties, Reactions, Production and Uses
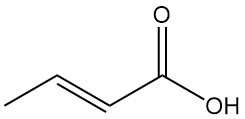
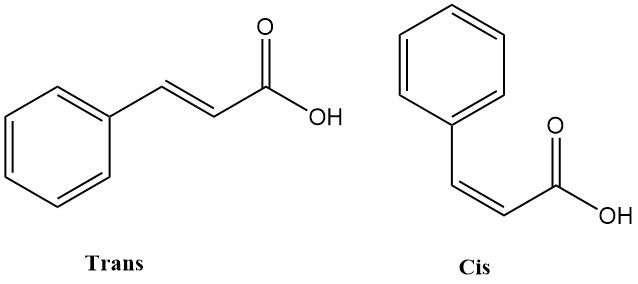
Crotonic acid is the trans-isomer of 2-butenoic acid. It is a short-chain, unsaturated carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3CH=CHCOOH. The cis isomer of 2-butenoic acid is known as isocrotonic acid.