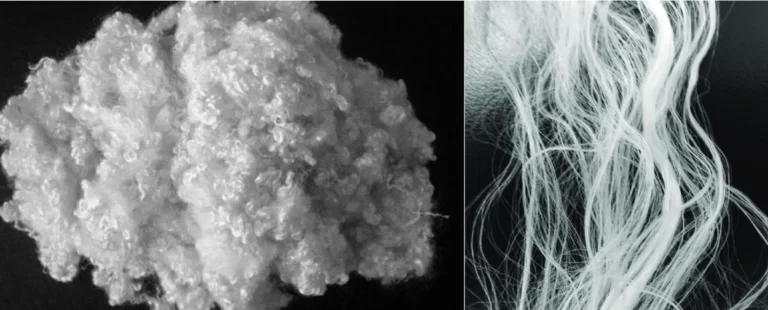
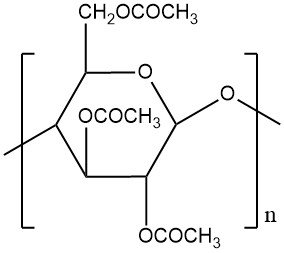
Cellulose Acetate Fibers: Properties, Production and Uses
cellulose acetate fibers are a type of synthetic fiber derived from cellulose. They are one of the earliest synthetic fibers ever developed and were once widely used in various applications. They are made by treating cellulose with acetic acid and acetic anhydride to create cellulose acetate, which is then dissolved in a solvent and spun into fibers through a dry spinning process.