1,4-Butanediol: Properties, Reaction, Production and Uses
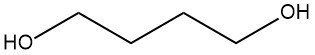
1,4-butanediol (often abbreviated as 1,4-BDO) is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C4H10O2. It is a colorless and odorless liquid that belongs to the family of diols, which are compounds that contain two hydroxyl (OH) groups.