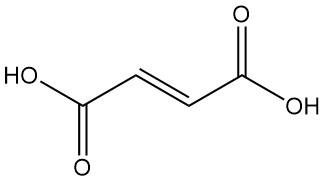
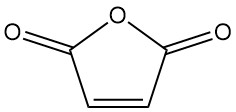
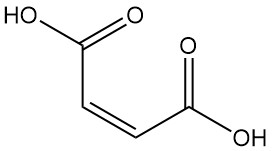
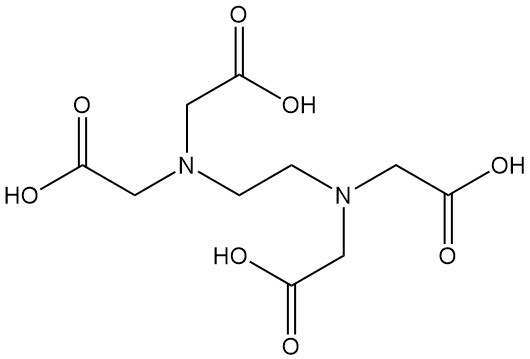
Mandelic Acid: Properties, Production and Uses
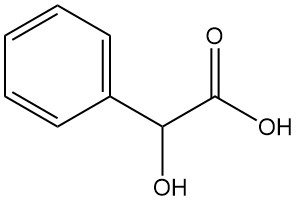
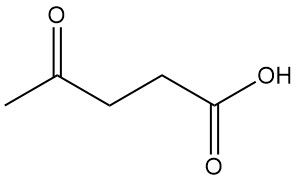
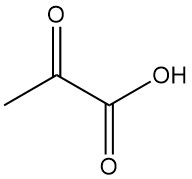
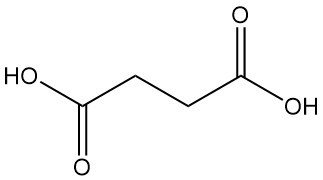
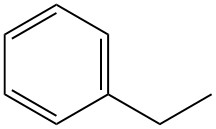
Mandelic acid, also known as α-hydroxyphenylacetic acid or phenylglycolic acid, is an aromatic alpha-hydroxy acid with the chemical formula C8H8O3. It is a white crystalline powder with a faint sweet odor.