Phenoxy Herbicides: Production, Uses and Toxicology
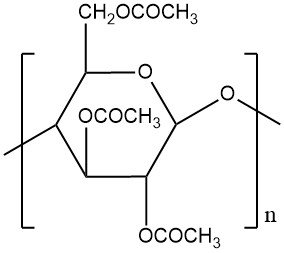
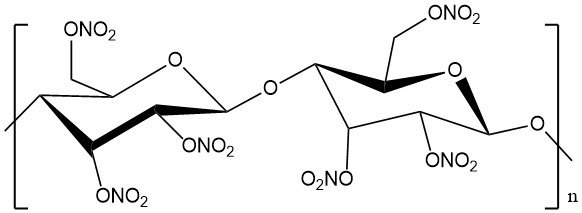
During World War II, research on chlorinated phenoxy compounds led to the discovery of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) as a selective herbicide. This discovery revolutionized weed control in grasses and related crops like cereals, rice, and sugarcane.