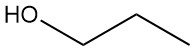
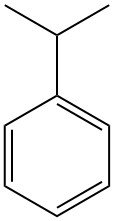
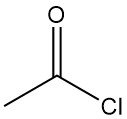
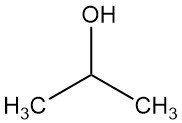
Sinopec: A profile of the world’s largest chemical producer
Sinopec, formally known as China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation, is a vertically integrated energy and chemical powerhouse headquartered in Beijing. As a majority state-owned enterprise, it serves as a critical pillar of China’s national energy security while simultaneously operating as the world’s largest oil refining group by capacity.