o-Cresol: Properties, Reactions, Production and Uses
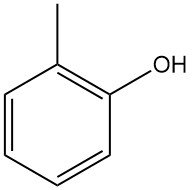
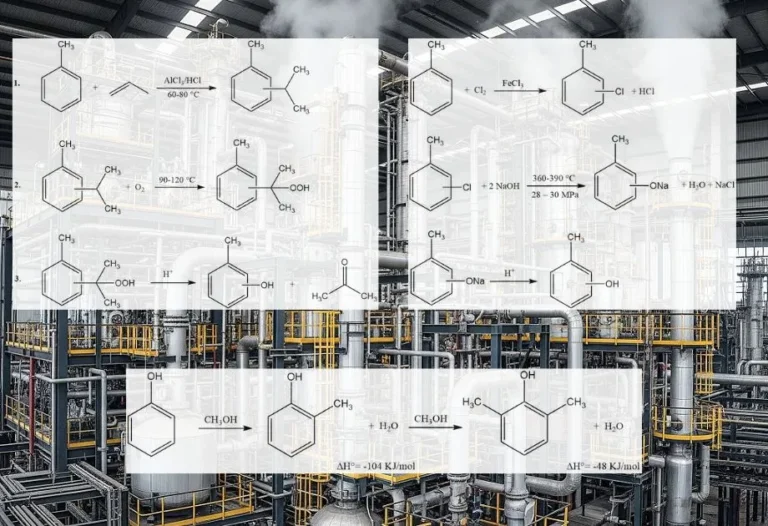
o-Cresol, also known as 2-methylphenol, is an organic compound with the chemical formula C7H8O. It is a colorless crystalline solid at room temperature with a phenolic odor that is highly soluble in most organic solvents.