Production Processes of Titanium Dioxide: a Complete Overview
Commercial titanium dioxide is manufactured via two distinct industrial methods: the sulfate process and the chloride process.
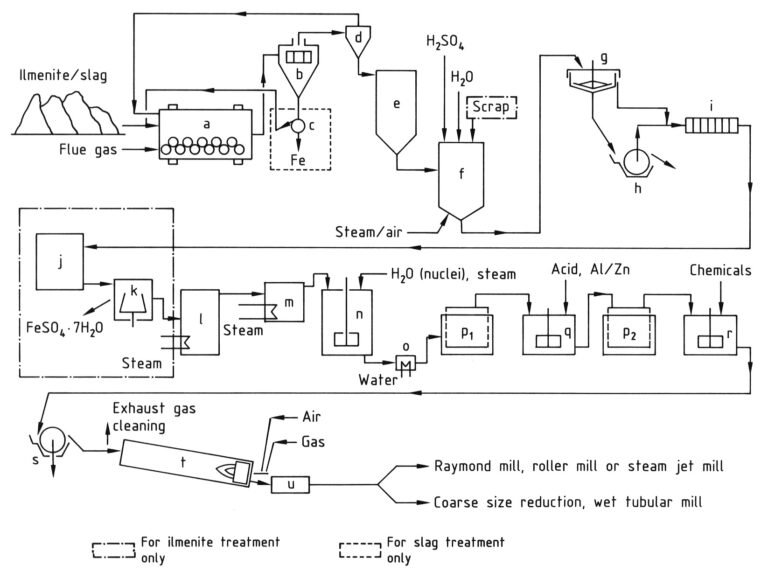
Commercial titanium dioxide is manufactured via two distinct industrial methods: the sulfate process and the chloride process.
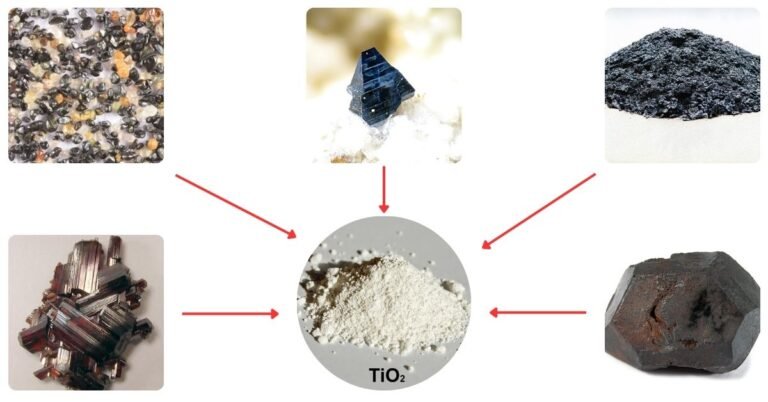

The raw materials for titanium dioxide production include natural products such as ilmenite, leucoxene, and rutile, and some very important synthetic materials such as titanium slag and synthetic rutile.
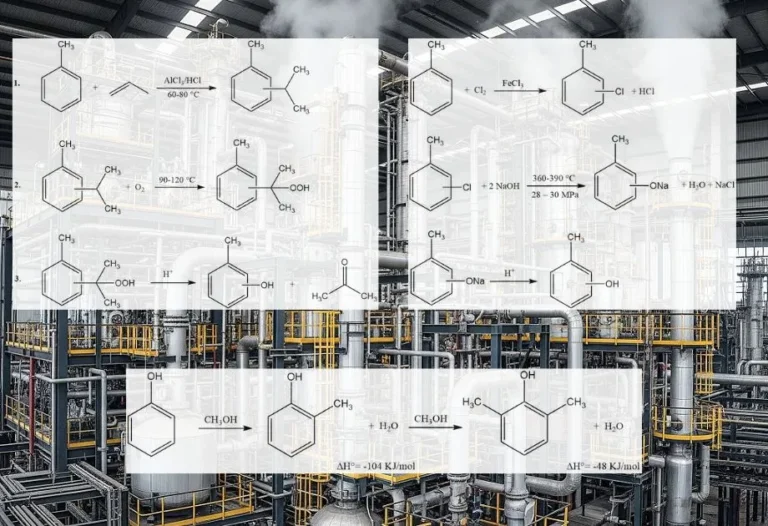
Cresols are primarily produced by different processes such as alkali fusion of toluenesulfonates, alkaline chlorotoluene hydrolysis, splitting of cymene hydroperoxide, and vapor-phase methylation of phenol.

In chemistry, acetylation is an organic reaction in which an acetyl group (CH3CO-) is introduced into a molecule. This reaction typically involves the use of acetic acid (CH3COOH) or acetic anhydride (CH3CO)2O as the acetylating agent. The resulting product is called acetate.

Caprolactam, the key ingredient in Nylon-6, can be produced by several routes. The most common method is the convertion of cyclohexanone to cyclohexanone oxime by ammoximation or hydrogen peroxide processes. This oxime then undergoes a Beckmann rearrangement to form caprolactam.

Acetylene is produced by several methods: calcium carbide reaction, partial combustion of hydrocarbons, electric arc processes, thermal cracking with heat carriers and as byproduct of steam cracking.
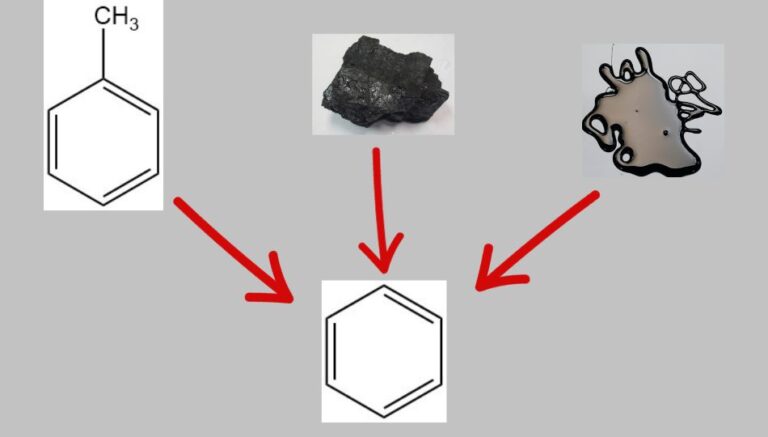

Benzene was traditionally produced from coal, but petroleum became the primary source in the mid-20th century due to new processes and increased demand. Catalytic cracking and reforming of petroleum fractions produce benzene and other aromatics.

Benzaldehyde condensation is a chemical reaction between benzaldehyde and an aldehyde or ketone molecules with an α-hydrogen to form an β-hydroxy aldehyde or ketone. The reaction is typically catalyzed by a strong base, such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide.

Amino resin production is a two-step process: hydroxymethylation and condensation. Hydroxymethylation is the addition of formaldehyde to an amino compound, such as urea, to form a hydroxymethyl derivative. Condensation is the reaction of two hydroxymethyl derivatives to form a larger molecule.
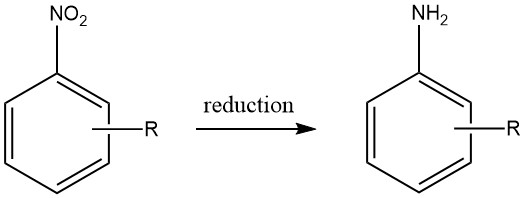
Aromatic amines are produced by three types of reactions:
Reductions: using metallic elements like Iron (Fe), Zinc (Zn), Tin (Sn), Aluminum (Al), or their corresponding salts; sulfur-containing compounds; electrochemical procedures; and catalytic hydrogenation.
Nucleophilic substitutions: involving the exchange of substituents like halogen, hydroxyl, alkoxy, and sulfonic groups.
Rearrangements and degradations: including transformations such as the benzidine and Beckmann rearrangements, along with the Schmidt and Hofmann degradations.
It should be noted that the first two reaction types are more important. Chemical rearrangements and degradations rarely result in pure reaction products with high yields.

The primary method of producing aldehydes is oxo synthesis, achieved by mild oxidation (dehydrogenation) of primary alcohols and specialized olefin oxidation processes. In the essential oils of various plants, trace amounts of aldehydes occur naturally. Acetaldehyde, a byproduct of alcohol fermentation, forms by the decarboxylation of the intermediary pyruvic acid.
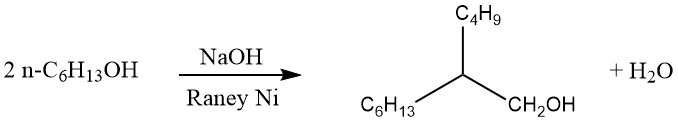
Production of aliphatic alcohols occurs by various industrial processes, some of which are listed below:
Synthesis from carbon monoxide and hydrogen (C1)
Oxo synthesis, often accompanied by hydrogenation of initially formed aldehydes (C3 – C20)
Hydrogenation of aldehydes, carboxylic acids, or esters
Aldol condensation of lower aldehydes followed by hydrogenation of the alkenals (C3 → C6, C4 → C8, C8 → C16)
Oxidation of trialkylaluminum compounds (Ziegler process)
Oxidation of saturated hydrocarbons
Hydration of olefins (C2–C4)
Homologation of alcohols
Hydrocarbonylation by the Reppe process
Hydrocarboxymethylation
Fermentation processes (C2–C5)
Guerbet process