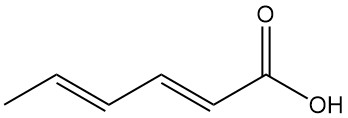
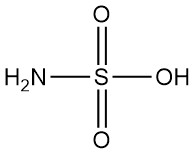
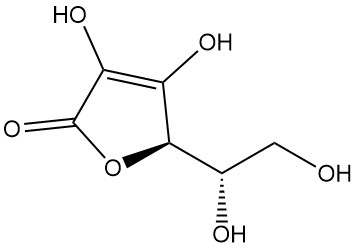
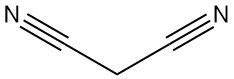
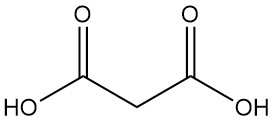
Thioglycolic Acid: Properties, Reactions, Production and Uses
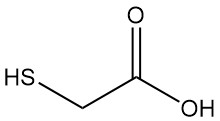
Thioglycolic acid, also known as mercaptoacetic acid, is the simplest and industrially most important mercaptocarboxylic acid with the formula HSCH2COOH. It is a colorless liquid with a strong, unpleasant odor.