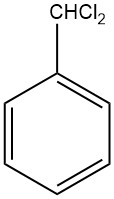
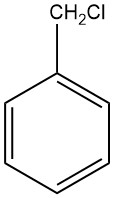
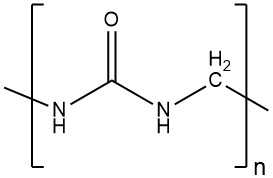
Anthracene: Properties, Production and Uses
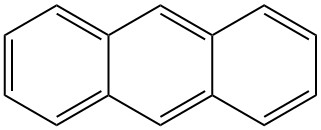
Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with the formula C14H10 that is composed of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal tar and was discovered in 1832 by J. Dumas and H. A. Laurent. Anthracene is colorless but exhibits a blue fluorescence under ultraviolet radiation.