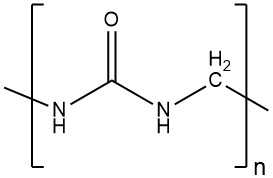
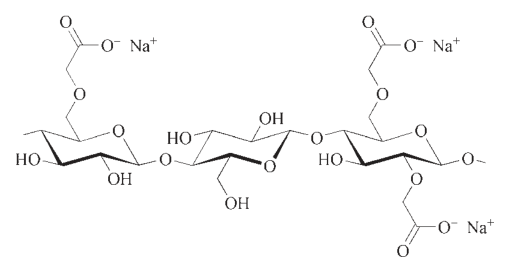
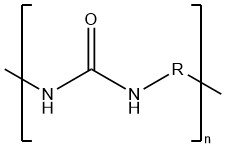
Toxicology of arsenic compounds
Arsenic compounds are generally toxic, especially inorganic ones. Some organic arsenic compounds used as chemical weapons are also highly toxic, but naturally occurring organic arsenic compounds in seafood are less so.