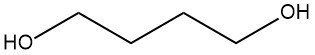
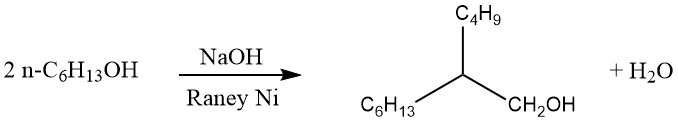
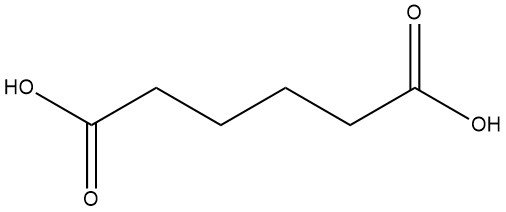
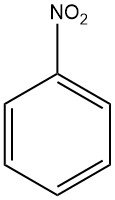
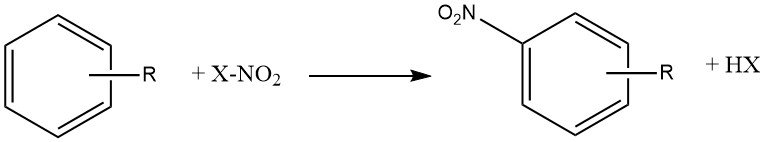
Production Methods of Aliphatic Aldehydes
The primary method of producing aldehydes is oxo synthesis, achieved by mild oxidation (dehydrogenation) of primary alcohols and specialized olefin oxidation processes. In the essential oils of various plants, trace amounts of aldehydes occur naturally. Acetaldehyde, a byproduct of alcohol fermentation, forms by the decarboxylation of the intermediary pyruvic acid.