Acetonedicarboxylic Acid: Properties, Production and Uses
What is Acetonedicarboxylic Acid?
Acetonedicarboxylic acid, also known as 3-oxoglutaric acid, 3-oxopentane dicarboxylic acid, or β-ketoglutaric acid, is a dicarboxylic acid with the formula C5H6O5. It is a crystalline solid that is soluble in water and alcohol.
Acetonedicarboxylic acid was first isolated and described by Van. Pechmann.
Table of Contents
1. Physical Properties of Acetonedicarboxylic Acid
Acetonedicarboxylic acid is a colorless, crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water and ethanol and less soluble in trichloromethane and diethyl ether. It decomposes at 138 °C.
All the known physical properties of acetonedicarboxylic acid are listed in the following table.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| CAS number | [542-05-2] |
| Chemical Formula | HOOC-CH2-CO-CH2-COOH |
| Molecular Weight | 146.10 g/mol |
| Melting Point | 133 °C |
| pKa1 | 3.33 |
| pKa2 | 4.27 |
| Flash Point | 200 °C (open cup) |
2. Chemical Reactions of Acetonedicarboxylic Acid
Acetonedicarboxylic acid undergoes chemical reactions characteristic of both carbonyl and carboxylic acid functions.
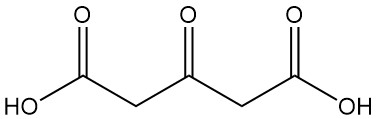
Acetonedicarboxylic acid is thermally decomposed at temperatures exceeding its melting point (133 °C) to produce carbon dioxide and acetone.
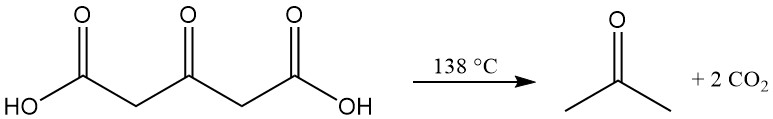
Aqueous solutions of acetonedicarboxylic acid are decomposed in two steps, producing acetoacetic acid as an intermediate, which subsequently decomposes to acetone and carbon dioxide. Metal ions and H+ catalyze this process.
Phenols react with acetonedicarboxylic acid under dehydrating conditions to form coumarin derivatives.
It can react with alcohols in the presence of an acid catalyst to form esters.
Acetonedicarboxylic acid can undergo self-condensation or condensation with other carbonyl compounds to form more complex products. It can form various derivatives, such as amides, hydrazides, and acid chlorides.
3. Production of Acetonedicarboxylic Acid
Acetonedicarboxylic acid is produced by the dehydration and decarboxylation of citric acid by fuming sulfuric acid. Vigorous cooling is applied to maintain a temperature between -5 °C and 10 °C during the reaction.
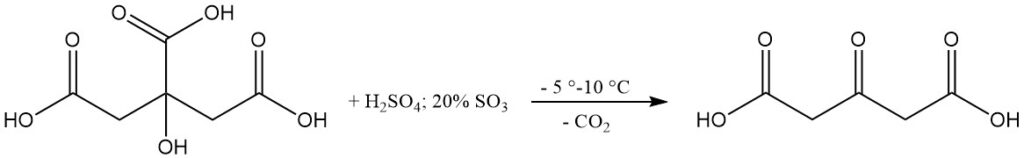
Temperature control is critical to preventing excessive reaction rates and product loss. The reaction mixture is subsequently warmed to induce gas evolution to about 30 °C before cooling and filtration.
Crude acetonedicarboxylic acid is obtained and purified by washing it with ethyl acetate. This process offers a good yield between 85 and 90%.
While the product can decompose, storage under anhydrous conditions can extend its stability, or it can be stored as esters.
Alternative production methods include the reaction between acetone and carbon dioxide, the oxidation of citric acid using chlorosulfuric acid, or the reaction of ketene with phosgene.
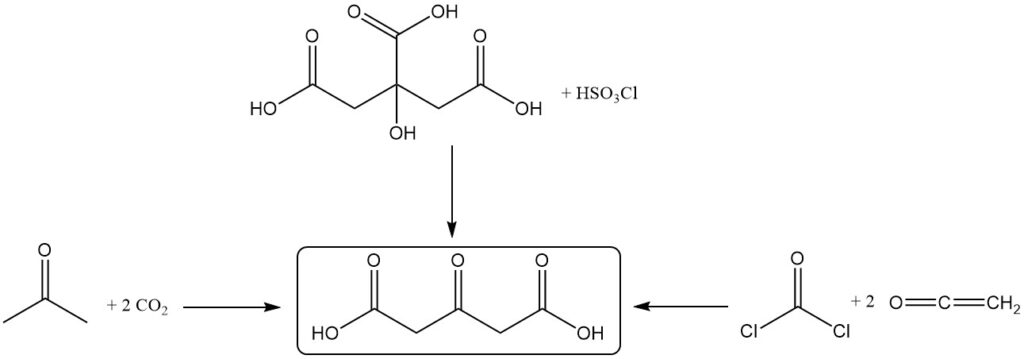
4. Uses of Acetonedicarboxylic Acid
Acetonedicarboxylic acid is used as a precursor in the production of pharmaceutical alkaloids. It is also a stabilizer used in natural oils and fats.
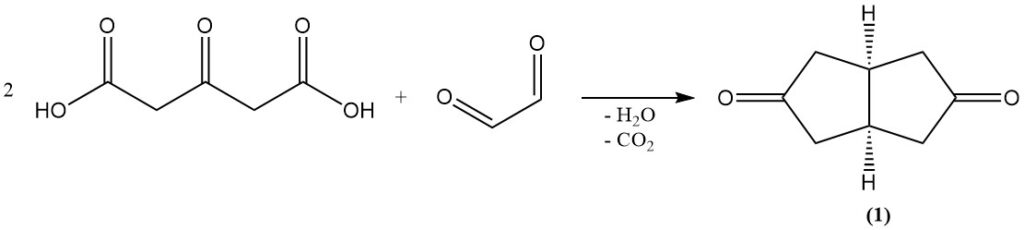
Acetonedicarboxylic acid is a fundamental building block in organic synthesis, contributing to heterocyclic ring formation and the Weiss-Cook reaction, which yields cis-bicyclo[3.3.0]octane-3,7-dione (1). It is also employed in the Robinson tropinone synthesis.
The presence of β-ketoglutaric acid in urine is an indication of the presence of harmful Candida albicans in the gut flora.
Acetonedicarboxylic acid also serves as a synthetic intermediate for benzodiazepines and hepatitis C virus polymerase inhibitors.
Acetonedicarboxylic acid functions as a stimulus for pH regulation in time-dependent processes.
5. Toxicology of Acetonedicarboxylic Acid
Acetonedicarboxylic acid is a corrosive substance capable of causing severe irritation and burns to the eyes, respiratory system, and skin upon contact.
Precautionary measures when handling acetonedicarboxylic acid include:
- Wear personal protective equipment (gloves, eye protection)
- Avoid skin and eye contact
- Wash thoroughly after handling
- Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated place
References
- Oxocarboxylic Acids; Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/14356007.a18_313
- https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/US/en/product/aldrich/165115
- https://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=CV1P0010
- https://chemistry-europe.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/syst.202300037
- https://www.fishersci.com/store/msds?partNumber=AC173150025&countryCode=US&language=en
