1,2-Butanediol: Properties, Production and Uses

1,2-Butanediol, also known as 1,2-butylene glycol, is an organic compound (diol) with the formula HOCH2(HO)CHCH2CH3. It is a colorless, viscous liquid with a slight odor.
Table of Contents
1. Physical Properties of 1,2-Butanediol
1,2-Butanediol (CAS Number: 584-03-2) is a colorless liquid with numerous industrial applications. Here are some of its key physical properties:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H10O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 90.12 g/mol |
| Melting Point | -50 °C |
| Boiling Point | 195-196.9 °C (at 101.3 kPa) |
| Density (20°C) | 1.0023 g/cm³ |
| Refractive Index (20°C) | 1.4382 |
| Solubility in water | Miscible in all proportions |
| Solubility in alcohols | Readily soluble |
| Solubility in ethers and esters | Slightly soluble |
| Solubility in hydrocarbons | Insoluble |
| Dynamic Viscosity (20°C) | 73 mPa·s |
| Flashpoint | 107 °C |
2. Chemical Properties of 1,2-Butanediol
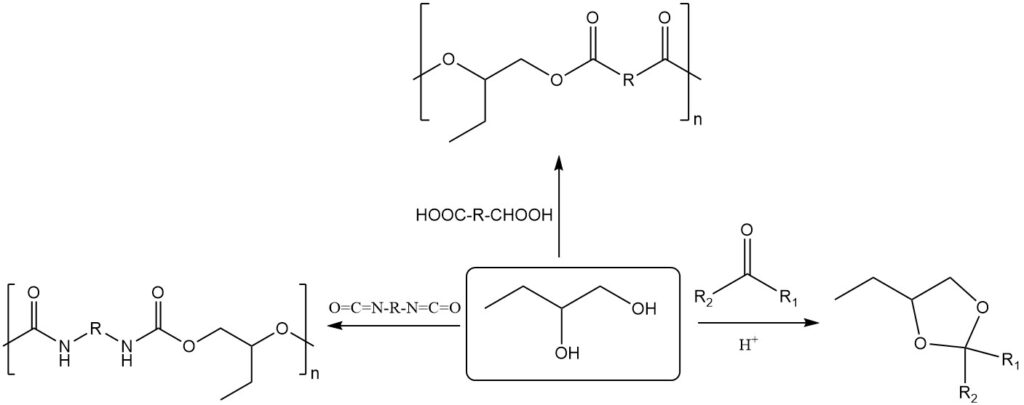
1,2-Butanediol exhibits typical glycol reactivity like 2,3-butanediol, readily forming acetals and ketals. Additionally, it reacts with dicarboxylic acids or anhydrides to form polyesters, and with diisocyanates to form polyurethanes.
The bacterium Gluconobacter oxydans DSM 2003 can efficiently produce (R)-2-hydroxybutyric acid (2-HBA) from 1,2-butanediol with high concentration (18.5 g/l) and good enantiomeric excess (99.7%).
3. Production of 1,2-Butanediol
1,2-Butanediol is synthesized by adding water to 1,2-epoxybutane. This exothermic hydration reaction (∆H = -93 kJ/mol) requires a 10- to 20-fold molar excess of water to prevent polyether formation.

Two primary production methods exist:
1. Without Catalyst: The reaction is carried out at 160-220 °C and 10-30 bar, eliminating the need for a catalyst.
2. With Catalyst: Catalysts like sulfuric acid or strongly acidic ion exchange resins can be used. This allows the reaction to occur below 160 °C and only slightly above atmospheric pressure.
Selectivity for 1,2-butanediol depends on the water excess, ranging from 70% to 92%. Higher ethers of 1,2-butanediol are formed as byproducts.
4. Uses of 1,2-Butanediol
While 1,2-butanediol has a modest range of direct applications, it is used as a solvent in the industrial process, as a chemical intermediate in the production of polymers and polyurethanes, and as a potential raw material for the synthesis of α-ketobutyric acid.
5. Toxicology
The median lethal dose (LD50) of 1,2-butanediol is 16 g/kg (rat, oral).
References
- Butanediols, Butenediol, and Butynediol, Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14356007.a04_455.pub2
- https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/en/tech-docs/paper/275866
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/1,2-Butanediol
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/1%2C2-butanediol
