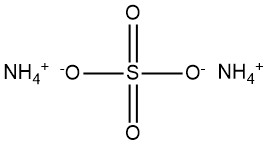
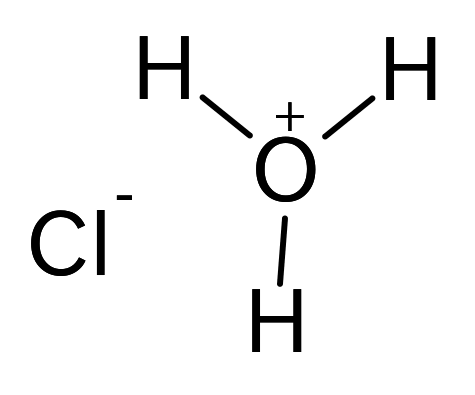
Boron trioxide: Properties, Production and Uses
Boron trioxide, also known as diboron trioxide, is the compound with the chemical formula B₂O₃. It is a colorless, transparent solid that is almost always glassy (amorphous), but can be crystallized with great difficulty.